Build our future with CO2.
O
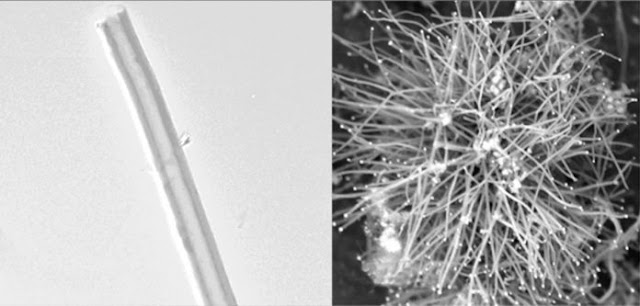
Scientists are converting carbon dioxide (CO2), a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change, into carbon threads. The threads are nanofibers, and they may be the building blocks of the future.
Stuart Licht, lead scientist on a George Washington University team researching this process, thinks making a strong, durable material from thin air can eventually become commercially viable.
His team found that carbon nanofibers are superior to steel in strength, flexibility and conductivity. That makes them useful for many applications — from batteries and electronics to lightweight, high-strength materials used in buildings, aircraft, cars and athletic equipment.
A new process uses solar power
It takes a few steps and renewable energy to transform CO2 to carbon nanofibers.
CO2 is captured from the air where emissions are heavy.
Solar energy provides the intense heat and electricity required to break down captured CO2 in a molten carbonate bath.
The CO2 dissolves when it contacts electrified electrodes.
The carbon nanofibers accumulate on the steel electrode.
Licht thinks the process could be done on a scale that would greatly reduce the amount of harmful CO2 emissions caused by human activity.
Please ! write your suggestions and interested topics in comment box.
If you want more information about this article please cooment in comment box.
Please, subscribe our website to support us to put interesting articles.
O
Scientists are converting carbon dioxide (CO2), a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change, into carbon threads. The threads are nanofibers, and they may be the building blocks of the future.
Stuart Licht, lead scientist on a George Washington University team researching this process, thinks making a strong, durable material from thin air can eventually become commercially viable.
His team found that carbon nanofibers are superior to steel in strength, flexibility and conductivity. That makes them useful for many applications — from batteries and electronics to lightweight, high-strength materials used in buildings, aircraft, cars and athletic equipment.
A new process uses solar power
It takes a few steps and renewable energy to transform CO2 to carbon nanofibers.
CO2 is captured from the air where emissions are heavy.
Solar energy provides the intense heat and electricity required to break down captured CO2 in a molten carbonate bath.
The CO2 dissolves when it contacts electrified electrodes.
The carbon nanofibers accumulate on the steel electrode.
Licht thinks the process could be done on a scale that would greatly reduce the amount of harmful CO2 emissions caused by human activity.
Please ! write your suggestions and interested topics in comment box.
If you want more information about this article please cooment in comment box.
Please, subscribe our website to support us to put interesting articles.
Build our future with CO2
 Reviewed by A civil Engineer
on
December 31, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by A civil Engineer
on
December 31, 2018
Rating:
 Reviewed by A civil Engineer
on
December 31, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by A civil Engineer
on
December 31, 2018
Rating:















No comments: